Design Diversity: From Duplexes to Fourplexes Living Space
This post is a summary of Eisa’s recent presentation at the 2nd Annual Modular for Multi-Family Housing Symposium.
As urban centers continue to grow and housing shortages become more pressing, multi-family housing has emerged as a viable solution to maximize land use while ensuring livability. From duplexes to fourplexes, these housing types offer increased density, affordability, and community-building potential. Modular construction, with its efficiency and sustainability, presents a compelling approach to realizing diverse multi-family housing solutions. This presentation explores how modular design can be leveraged to create well-designed, functional, and code-compliant housing.
Understanding Multi-Family Housing and Its Importance
Multi-family housing refers to residential buildings with multiple separate housing units, often within the same structure. These homes provide an alternative to single-family dwellings, offering cost-effective and space-efficient solutions in growing cities. Duplexes, triplexes, and fourplexes serve as a "missing middle" between single-family homes and larger apartment buildings, addressing the increasing demand for attainable housing.
The advantages of these housing types include shared infrastructure costs, optimized land use, and the ability to create more diverse and inclusive communities. In cities struggling with housing shortages, multi-family dwellings present a pathway to meeting the needs of a growing population without the sprawl associated with single-family developments.
Design Basics for Duplexes, Triplexes, and Fourplexes
Each multi-family housing type presents distinct challenges and opportunities, particularly in modular construction, where standardization must balance with design flexibility.
Duplex Design Considerations
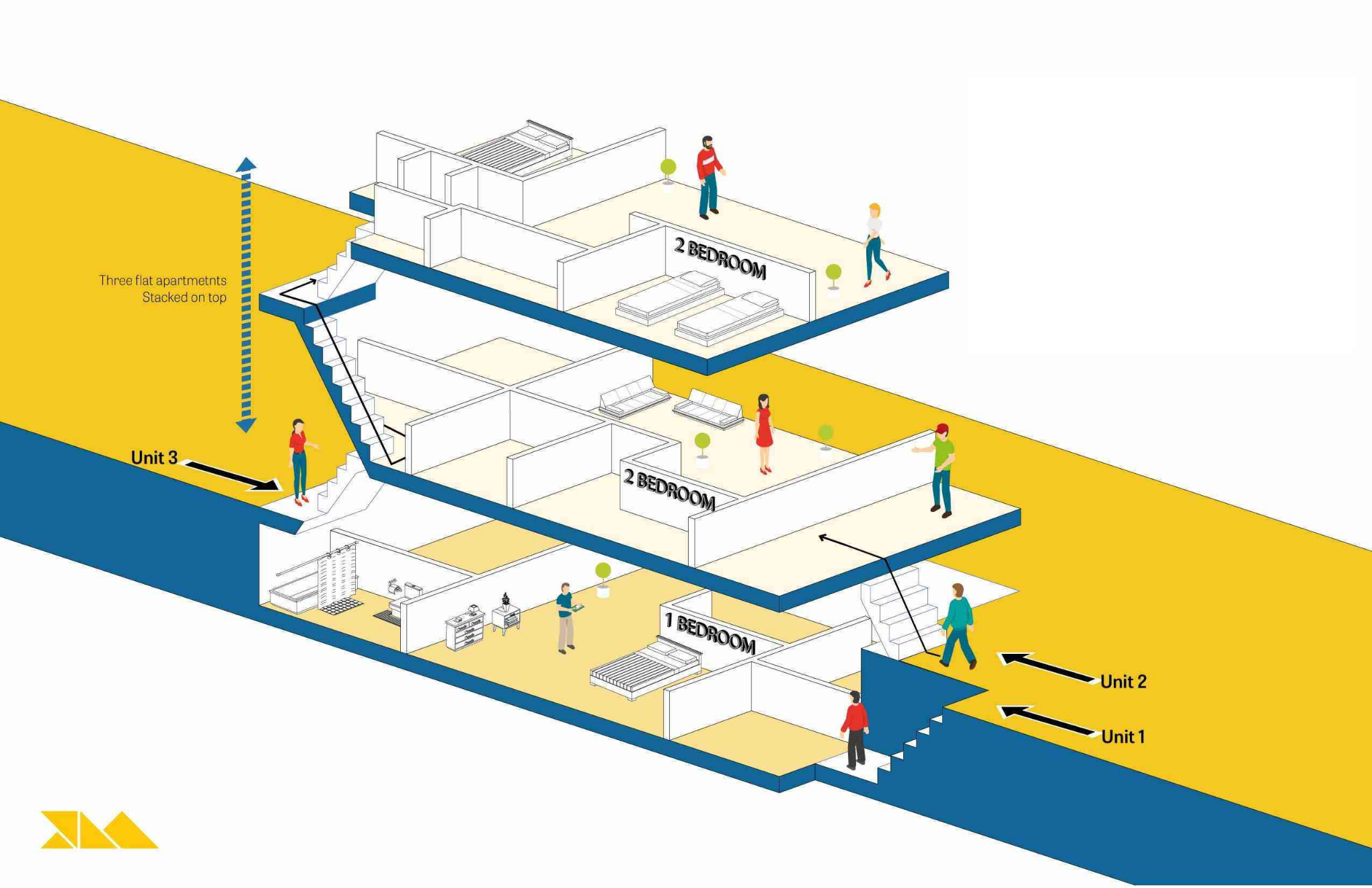
A duplex consists of two housing units sharing a common wall, either side-by-side or stacked vertically.
Privacy and Noise Control: Modular construction enables precise integration of soundproofing materials, enhancing occupant comfort.
Shared Infrastructure: Efficient mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEP) coordination ensures cost-effective construction.
Maximizing Livability: Thoughtful modular layouts ensure optimal unit layouts without wasted space.
Example: A modular duplex on a typical lot can be designed with independent entrances or a shared foyer to optimize site constraints.
Triplex Design Considerations
A triplex consists of three separate units, often configured with individual entrances or a shared central stairwell.
Space Efficiency: Layouts must prioritize functionality while ensuring adequate natural light and privacy.
Structural Coordination: Load-bearing walls and module matelines must align to enhance efficiency without requiring extensive on-site modifications.
Flexible Entrances: Individual exterior doors provide privacy, while a shared stairwell consolidates circulation spaces.
Example: A modular triplex with stacked units benefits from shared utility chases and streamlined modular assembly.
Fourplex Design Considerations
A fourplex features four units, either stacked or arranged around a shared entry.
Code Compliance: In Ontario, structures with three or more units fall under stricter fire separation and egress requirements.
Design Efficiency: A common stairwell layout allows for more compact circulation areas, while direct exterior entrances enhance accessibility.
Modular Benefits: Off-site fabrication ensures that units adhere to fire code standards before arriving at the site.
Example: A volumetric modular fourplex maximizes land use while ensuring rapid assembly with pre-approved fire-rated wall assemblies.
OBC Compliance and Design Challenges
In Ontario, any building with three or more units is classified as a small building under the Ontario Building Code. This classification introduces more stringent requirements for fire safety, exit strategies, and building envelope performance. Key considerations include:
Exposed building face construction: Ensuring fire-resistance ratings align with lot setbacks and adjacent structures.
Two exit strategies: Triplexes and fourplexes require clear and accessible means of egress, often addressed through well-planned stairwells and shared corridors.
Plumbing strategies: Shared plumbing stacks simplify installation, while individual plumbing stacks enhance fire separation compliance.
The Role of Modular Construction in Multi-Family Housing
Modular construction consists of two primary methodologies: volumetric modular systems and panelized systems.
Volumetric modular construction involves the off-site fabrication of entire room-sized modules, which are then transported to the site and assembled. This method significantly reduces construction time and improves quality control.
Panelized systems involve pre-constructed wall, floor, and roof panels assembled on-site, offering flexibility in internal layouts and design adaptability.
Both systems contribute to reducing waste, improving efficiency, and minimizing the environmental impact of construction. Modular buildings also allow for streamlined workflows, ensuring consistent quality and adherence to local building codes.
And when it comes to multi-family housing, both modular approaches offer unique benefits:
Panelized systems provide greater flexibility in interior layouts since structural gridlines do not need to align across floors.
Volumetric modular design minimizes on-site work, reducing neighbourhood disruptions and enabling faster occupancy.
Modular construction offers a transformative approach to designing and delivering efficient, sustainable, and cost-effective multi-family housing. By addressing design challenges, adhering to strict building codes, and leveraging industrialized construction techniques, modular duplexes, triplexes, and fourplexes can play a crucial role in meeting housing demands in growing urban centers.
As modular technology advances and regulatory frameworks adapt, the future of diverse, well-designed multi-family housing will increasingly rely on off-site construction methodologies—ensuring faster, more efficient, and more accessible homes for communities worldwide.
•••
XLBench is your go-to platform for modular construction insights, setting industry benchmarks, fostering expert discussions, and sharing the latest trends. Through Benchboard, we provide data-driven research, thought leadership, and in-depth analysis to advance modular innovation.
Stay informed and be part of the conversation—follow XLBench for the latest updates, expert insights, and industry trends.
•••
xL Architecture & Modular Design (XLA) is an innovative architecture firm redefining the future of building through off-site construction technologies. With expertise in volumetric modular designs, and panelized building systems, we create cutting-edge solutions that seamlessly integrate form, function, and sustainability.